A comprehensive analysis of how recent U.S. tariff policies are reshaping global trade dynamics and what business leaders need to know, Trump Tariffs 202.
U.S. President Donald Trump’s recent implementation of sweeping tariffs has sent unprecedented ripples through global markets, wiping out approximately $2.5 trillion in market value in a single day. This seismic economic event has triggered retaliatory measures worldwide and created a complex new reality for international business. Our analysis explores the far-reaching consequences across regions and industries, offering strategic insights for business leaders navigating this volatile landscape.
Before diving into the subject, recent news, and its impact, let’s first understand some terminology and key concepts about tariffs, along with a brief history.
What exactly is a tariff war?
A tariff war occurs when countries impose escalating import taxes against each other in a cycle of retaliation. This process typically begins with one nation implementing protective tariffs, followed by countermeasures from affected trading partners, potentially leading to broader economic disruption as costs increase throughout global supply chains.
What is the tariff war meaning for global businesses?
The tariff war meaning for businesses includes several critical dimensions:
- Increased costs for imported components and materials
- Disrupted supply chains requiring potential restructuring
- Market access challenges in countries imposing retaliatory tariffs
- Strategic opportunities to capture market share as competitors face tariff pressure
- Necessity to engage with government trade officials to seek exemptions or adjustments
What lessons can we learn from tariff wars in history?
Tariff wars in history, particularly the Smoot-Hawley Tariff of 1930, demonstrate that aggressive protectionism typically:
- Reduces overall economic growth
- Increases consumer prices
- Leads to retaliatory measures that harm exporters
- Creates economic inefficiencies as production shifts to less optimal locations
- Eventually requires negotiated settlements to restore trade flows
- Can contribute to diplomatic tensions beyond the economic sphere
The Tariff Aftermath: Unprecedented Market Volatility
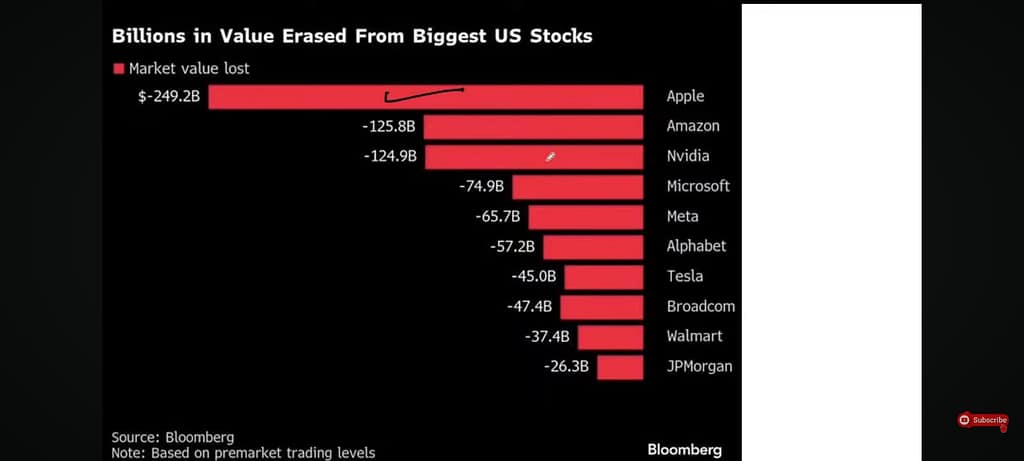
Recent aggressive tariffs imposed on over 60 countries have caused a huge market shock. Major indices, like the NASDAQ and S&P 500, experienced some of their worst one-day declines since 2020. In just 24 hours, around $2.5 trillion in market value vanished. This sudden policy change has created a lot of uncertainty, leading many big investors to look for safer options.
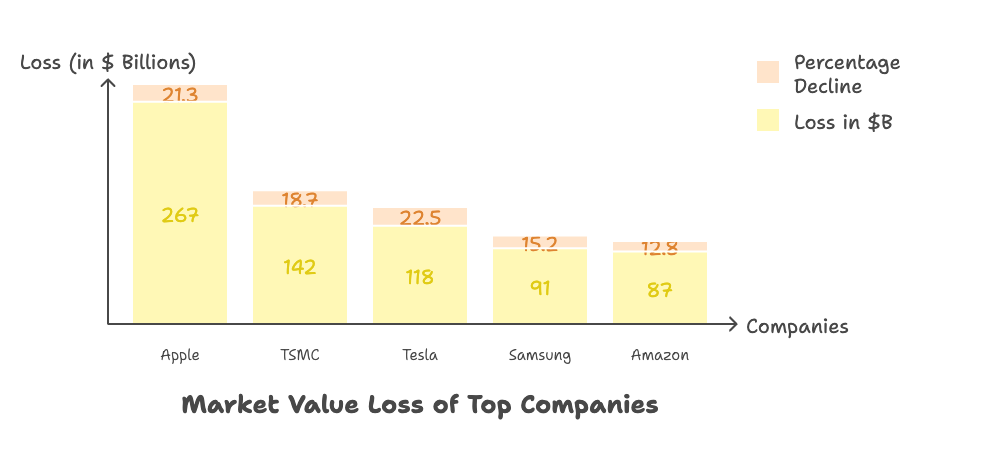
Top 5 Companies Hit Hardest Last Week
- Apple Inc. – Lost $267 billion in market capitalization (21.3% decline), as concerns mounted about both their Chinese manufacturing exposure and potential retaliatory measures affecting their critical Chinese consumer market.
- TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) – Suffered a $142 billion market value drop (18.7% decline), as the world’s largest semiconductor manufacturer faces disruptions to its complex global supply chain and customer base.
- Tesla, Inc. – Experienced a $118 billion valuation decrease (22.5% decline), due to its dual vulnerability from Chinese component sourcing and China representing its second-largest market globally.
- Samsung Electronics – Recorded a $91 billion market value reduction (15.2% decline), with investors concerned about its extensive manufacturing presence across multiple tariff-affected regions.
- Amazon.com, Inc. – Saw an $87 billion market cap erosion (12.8% decline), as its vast global logistics network and reliance on imported consumer goods face significant cost increases.
Sector-Specific Impact Analysis- globally
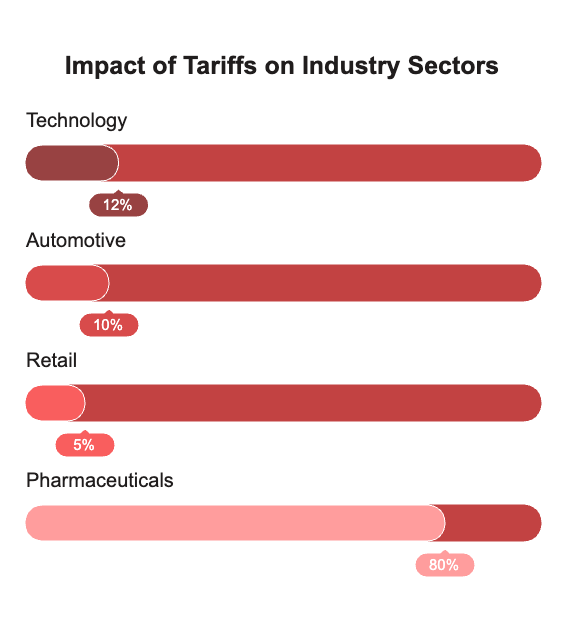
Technology
Silicon Valley has been particularly hard hit by the tariff policies, with semiconductor companies seeing an average 12% decline in share value. Companies like Nvidia, AMD, and Intel, which rely heavily on global supply chains, have experienced significant disruptions. Apple, with its substantial manufacturing presence in China, saw its market cap decrease by over $200 billion within days of the announcement.
Automotive
Major automakers including Tesla, Ford, and General Motors have warned of price increases between 5-15% on new vehicles due to higher costs for imported components. European luxury brands like BMW and Mercedes-Benz are reconsidering their U.S. manufacturing investments, potentially affecting thousands of American jobs.
Retail
Walmart, Target, and Amazon have all indicated that consumers will ultimately bear the burden of these tariffs. The National Retail Federation estimates that the average American household could face additional costs of $1,200 annually due to higher prices on imported goods.
Pharmaceuticals: A Global Health Crisis Looming
The pharmaceutical sector, once thought to be safe from trade disputes, is now facing big problems that could affect many people’s health. Major companies like Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and AstraZeneca are seeing increased costs and delays in production.
Pfizer, for example, reports that 80% of its ingredients face tariffs, while Johnson & Johnson estimates an extra $1.2 billion in annual costs. These issues also impact the production of vaccines and antibiotics, causing worries about delays and higher prices.
These tariff problems could lead to a serious healthcare crisis. Essential medications like antibiotics, diabetes treatments, hypertension drugs, HIV/AIDS therapies, and childhood vaccines are all expected to see price increases.
Low and middle-income countries, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa, rely on affordable medicine, but a rise in prices could mean fewer people get the help they need. Organizations like Médecins Sans Frontières predict a funding gap of $1.7 billion to keep distributing these vital medications.
Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus from the World Health Organization warns that this situation is more than just a trade dispute—it could become a public health disaster. He explains that when essential medicines are too expensive, preventable deaths happen.
The World Health Organization notes that a 10% price increase usually leads to a 12-14% drop in access for vulnerable populations. This means that many people might not be able to get the medicines they need, leading to serious health issues worldwide.
India’s Critical Role
India’s pharmaceutical industry could help solve this crisis. Indian companies make 20% of the world’s generic drugs and 40% of the generic medicines used in the U.S. If China can’t supply these medicines, India could fill 60-70% of the gap.
India’s drug export council, says they can increase production by 35% in a year. Dilip Shanghvi, founder of Sun Pharmaceutical, says India is ready to help and can quickly scale up production.
The disruptions may change how medicines are provided worldwide. Foundations like the Gates Foundation are looking to work more with Indian manufacturers to avoid tariff issues and keep supplies steady.
The UN’s Medicines Patent Pool is speeding up licensing agreements for crucial drugs, and new financing methods are being developed to cover higher production costs so that people in need aren’t affected. The World Bank warns that without action, 18.2 million people in low-income countries might lose access to vital medicines by mid-2026.
These tariff problems have serious implications for global health. Many foundations and organizations are working hard to find solutions. India’s pharma sector is prepared to step in and make sure that crucial medicines remain available worldwide. This coordinated effort is essential to prevent a healthcare disaster and ensure that everyone continues to receive the medication they need.
Global Retaliation: The Mounting Response
China’s Strategic Countermeasures: Beyond Tit-for-Tat
China has responded strategically to the U.S. tariffs, going beyond just matching them. Initially, it imposed equivalent tariffs on $120 billion worth of U.S. exports, focusing on agricultural products, aircraft components, and luxury vehicles.
They also speeded up reviews for another $85 billion in potential tariffs. Next, China suspended $7.2 billion in planned agricultural purchases from the U.S. and increased customs clearance times for U.S. goods from 3 days to 12 days.
Additionally, they started “quality and safety” reviews of U.S. pharmaceuticals and medical devices, impacting $14.3 billion in annual exports. China’s strategic moves include hinting at export restrictions on rare earth minerals, which they dominate globally, and creating an “Unreliable Entity List” possibly targeting major U.S. companies like Boeing, Apple, and Intel. They also accelerated subsidies for domestic semiconductor development.
Diplomatically, China postponed high-level economic talks and announced $31 billion in funds to stabilize Chinese companies affected by U.S. market exposure. There are also discussions about devaluing the yuan, with a 4.2% depreciation already observed.
Dr. Elizabeth Economy from the Hoover Institution notes that China is showing strategic patience, calibrating its response to maintain control over escalation while highlighting its significant economic power. The Chinese Commerce Ministry has stated that their actions depend on U.S. behaviour and are ready for sustained measures if needed.
This response has caused market impacts, such as a drop in U.S. soybean and corn futures, Boeing shares falling, and reduced orders for Apple suppliers. The People’s Bank of China reports increased capital outflows, prompting new controls and stabilization measures.
European Union: Coordinated and Calibrated Counteraction
The European Union (EU) has responded to the U.S. tariffs with careful and coordinated actions. First, they quickly started assessing the impact and preparing their legal response.
Within just 6 hours, the European Commission activated its Trade Defence Instruments Committee and identified €68.7 billion worth of vulnerable exports. They also filed a formal complaint with the World Trade Organization (WTO) about the U.S. tariffs.
Next, the EU announced 25% tariffs on €18.4 billion of U.S. goods, choosing products that would politically affect key U.S. states. These included bourbon and whiskey from Kentucky and Tennessee, dairy products from Wisconsin, vehicles from Michigan, and energy equipment from Texas. They also increased scrutiny of U.S. technology companies.
The EU then moved quickly to strengthen economic ties with other regions. They accelerated negotiations with China, fast-tracked trade discussions with MERCOSUR, India, and ASEAN, and announced €45 billion in support measures for affected European industries. Specific funds were allocated to automotive manufacturing, precision machinery, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals.
Individual EU member states took additional actions. Germany announced a €12.7 billion incentive package to bring manufacturing back from the U.S. France sped up regulatory approvals for companies relocating from the U.S. Italy set up a €5.8 billion fund to support local alternatives to U.S. agricultural imports. Spain launched a €4.2 billion renewable energy initiative to reduce dependency on U.S. technology.
These actions have had real economic impacts. U.S. exports to Europe dropped by 12.3% in the first week after the countermeasures. The euro gained strength against the dollar, and European bond yields decreased as investors sought safe investments. The European Central Bank predicts that if tensions persist, EU GDP could drop by 0.4%, while the U.S. GDP might decline by 0.7%.
India: Sector-by-Sector Impact Analysis
India’s calculated response to the tariff situation shows its growing importance in the world economy. India announced careful 15-20% tariffs on select U.S. imports while pursuing aggressive trade diversification.
Information Technology Services
The IT sector faces a risk of $12.7 billion in potential revenue. TCS expects a 6.2% revenue impact, Infosys is estimating a 7.1% vulnerability, Wipro is projecting an 8.3% risk, and HCL Technologies anticipates a 5.8% exposure due to their reliance on U.S. clients. N. Chandrasekaran, Chairman of Tata Sons, believes this situation speeds up client conversations about nearshoring and automation and aligns with their shift toward consulting and AI services.
Pharmaceuticals
India has the chance to expand its market by $4.2 billion. Sun Pharmaceutical is positioned to gain $780 million, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories expects $620 million, Cipla forecasts $540 million, and Aurobindo Pharma estimates $490 million in growth. A report suggests India’s share of the U.S. generic drug market could rise significantly as supply chains adapt.
Automotive Components
The automotive sector sees a $2.1 billion export opportunity. Motherson Sumi has secured $340 million in new contracts, Bharat Forge is reporting $290 million in new orders, and Tata AutoComp projects a $215 million revenue increase from various components.
Textiles and Apparel
The textile sector has the potential for $3.7 billion in export growth. Aditya Birla Fashion has secured $210 million in new orders, Raymond Ltd reports a 23% increase in U.S. order inquiries worth $180 million, and Arvind Limited projects $240 million growth. U.S. buyers are shifting orders from China to India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh, and India is positioned to capture a significant portion of this opportunity.
Other Asian Nations
Japan and South Korea, traditionally close U.S. allies, have expressed deep concerns, with Tokyo announcing a 20% tariff on select American imports and Seoul reviewing its semiconductor cooperation agreements.
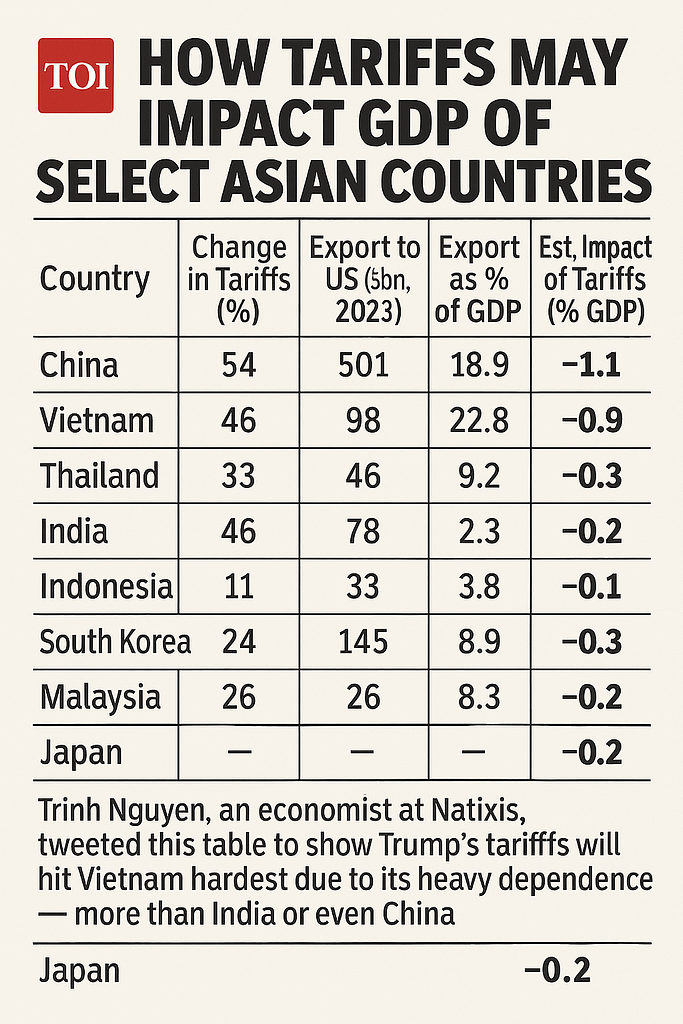
Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia – countries that had benefited from previous U.S.-China trade tensions – now face their own tariff challenges, potentially undermining their recent manufacturing gains. The ASEAN bloc is considering a unified response to maintain regional economic stability.
African Markets
While direct U.S.-Africa trade is comparatively smaller, secondary effects are significant. South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria, leveraging the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), face potential disruptions to their U.S. export channels. African Development Bank reports suggest the tariffs could slow the continent’s GDP growth by 0.4% as global investment contracts.
Strategic Business Implications
Supply Chain Reconfiguration
The era of globally optimized supply chains is giving way to regional resilience. Companies like Samsung and LG have already announced plans to relocate portions of their manufacturing from China to countries less affected by the tariffs, including Mexico, Vietnam, and India.
Pricing Strategy Recalibration
CFOs across industries are conducting emergency reviews of pricing strategies. The consensus approach involves a blend of absorbing some costs internally while selectively passing others to consumers, with most companies targeting a 40-60% pass-through rate based on competitive positioning.
Investment Portfolio Adjustments
Asset managers are rapidly rebalancing portfolios, with a notable shift toward domestically-focused companies and inflation-resistant assets. Goldman Sachs and BlackRock have both issued guidance suggesting reduced exposure to multinational corporations with significant tariff vulnerability.
Forward-Looking Strategies for Business Leaders
- Conduct Comprehensive Tariff Exposure Assessment: Quantify both direct and indirect tariff exposure throughout your entire value chain.
- Explore Geographic Diversification: Evaluate alternative manufacturing and sourcing locations, with particular focus on countries maintaining favorable trade relationships with both the U.S. and China.
- Accelerate Automation Initiatives: Increased labor costs due to reshoring may be partially offset through strategic automation and digitalization.
- Engage in Scenario Planning: Develop contingency plans for various escalation scenarios, including potential currency manipulations and non-tariff barriers.
- Leverage Trade Agreements: Identify opportunities within existing trade agreements that may provide tariff relief or preferential market access.
- Monitor Political Developments: Establish dedicated teams to track policy changes and engage constructively with relevant government stakeholders.
The WTO Factor: A System Under Strain
The World Trade Organization faces an existential challenge as bilateral tariff disputes undermine its multilateral framework. With its dispute resolution mechanism already weakened by U.S. opposition to judge appointments, many experts question whether the organization can effectively mediate the current tensions.
“We’re witnessing the potential unraveling of the post-WWII trade architecture,” warns former WTO Director-General Pascal Lamy. “Business leaders should prepare for a more fragmented global trading system with increasing bilateral arrangements replacing multilateral frameworks.”
India’s Strategic Inflection Point: From Challenge to Opportunity
India’s Strategic Inflection Point: From Challenge to Opportunity
India is seeing big changes in its economy because of global trade tensions. For instance, Apple wants to make 35% more iPhones in India, which is worth $12 billion, and Samsung is planning to expand its Noida factory by $4.2 billion.
Major pharmaceutical companies are also looking to invest $8.7 billion in India over the next three years. Car manufacturers like Toyota, Volkswagen, and Hyundai are starting programs to source $6.2 billion worth of components from India. Minister Piyush Goyal believes this shift could make India the world’s pharmacy and factory.
Digital Services Transformation
India’s tech industry is growing despite challenges. Big IT firms like TCS, Infosys, and Wipro are seeing more demand for consulting as companies try to save money due to tariffs. Since tariffs began, 42 new tech centers have been set up in India with $1.8 billion in investment.
Indian software companies are getting more business as U.S. companies look for cheaper options. NASSCOM thinks India’s tech sector could grow even faster, from 8.2% to 11.4% each year, as businesses focus on digital efficiency.
Diplomatic and Strategic Elevation
India’s careful approach to global trade issues is boosting its international standing. Deals with Australia and the U.S. for processing rare earth minerals worth $3.4 billion could make India a key player outside China.
The Quad alliance with the U.S., Japan, and Australia is getting stronger with new trade and supply chain agreements. European Union negotiators are also eager to speed up a free trade agreement with India to secure alternative supply chains.
Domestic Economy Resilience
India’s large internal market is helping it stay strong despite global challenges. Domestic consumption is expected to grow by 7.2%, thanks to a growing middle class. The government is spending $24 billion on infrastructure to support the economy.
Even though global markets are struggling, Indian stock indices have done better than global benchmarks by 8.3% since tariffs started. S&P Global suggests that these changes might help India become a $5 trillion economy by 2026, two years earlier than expected.
Navigating the New Normal
The market consequences of Trump’s tariff policies represent more than a temporary disruption—they signal a fundamental restructuring of global trade dynamics. Business leaders must recognize this is not a passing storm but rather a changed climate requiring comprehensive strategic adaptation.
While near-term market volatility will continue, forward-thinking organizations that proactively address supply chain vulnerabilities, diversify manufacturing footprints, and engage constructively with policymakers will emerge stronger. The coming years will likely Favor companies with agile operating models and regional self-sufficiency over those optimized purely for cost efficiency in a barrier-free global market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current status of Trump tariff on China?
The Trump tariff on China represents the most aggressive component of the current trade policy, with a blanket 34% tax on Chinese imports. This has prompted equivalent retaliatory measures from Beijing targeting $120 billion in U.S. exports, particularly agricultural products, aircraft components, and technology items. The situation continues to escalate with China considering rare earth mineral export restrictions.
What are Trump tariffs India policies?
Trump tariffs India policies include import taxes averaging 20% on Indian goods entering the U.S. market, primarily affecting textiles, pharmaceuticals, automotive components, and information technology services. India represents a significant but not primary target in the broader tariff strategy.
What is the Trump tariffs impact on India’s economy?
The Trump tariffs impact on India is mixed. While the IT services sector faces headwinds with potential revenue impacts of $12.7 billion (8.4% of sector exports), India’s pharmaceutical and manufacturing sectors may benefit as companies seek alternatives to Chinese suppliers. Overall, India’s large domestic market provides some insulation from global trade disruptions.
How serious is the current tariff war Trump has initiated?
The tariff war Trump has initiated represents one of the most significant disruptions to global trade since the 1930s. With approximately $2.5 trillion in market value lost in a single day following the announcement and retaliatory measures from multiple major economies, economic analysts rate this as an extremely serious trade conflict with potential long-term structural impacts.
What is the current state of the tariff war between US and China?
The tariff war between US and China has escalated to unprecedented levels. Following Trump’s implementation of 34% tariffs on Chinese goods, Beijing has responded with equivalent measures targeting politically sensitive U.S. exports. China has also implemented non-tariff barriers including enhanced customs inspections, regulatory reviews, and potential export restrictions on critical materials. The conflict shows no signs of de-escalation in the near term.
Where can I find the latest tariff war news?
The most current tariff war news can be found through financial news services, government trade publications, and industry-specific reports. Major developments are typically announced through official channels including the USTR, Chinese Ministry of Commerce, and equivalent bodies in the EU and other major economies.
What is the projected global GDP impact of Trump’s tariff policy?
Economic analysts estimate that continued implementation of Trump’s tariff policy could reduce global GDP growth by 0.8-1.2% over the next 12-18 months, with disproportionate impacts on export-dependent economies and those deeply integrated into global supply chains.
How are multinational corporations responding to Trump tariff uncertainty?
Multinational corporations are implementing multi-faceted responses to Trump tariff uncertainty, including supply chain diversification, strategic inventory buildup, pursuit of country-of-origin adjustments, and in some cases, price increases to consumers to offset higher input costs.
What is the Trump tariff strategy intended to accomplish?
The stated objectives of the Trump tariff strategy include reducing the U.S. trade deficit, reshoring manufacturing jobs, pressuring trading partners into bilateral agreements more favourable to American interests, and strengthening domestic industries considered critical to national security.
How will Trump tariffs affect consumer electronics prices?
Consumer electronics prices are projected to increase by 12-18% due to Trump tariffs, with particularly significant impacts on smartphones, laptops, and home entertainment systems that rely heavily on components manufactured in tariff-affected countries.
What is the projected impact of Trump tariffs on automotive industry?
The automotive industry faces potential price increases of 8-15% on new vehicles due to Trump tariffs, with complex global supply chains making this sector particularly vulnerable to trade disruptions. Major manufacturers have warned that these increased costs will ultimately be passed to consumers.
How will Trump’s protectionism affect renewable energy development?
Trump’s protectionism targeting solar panels, wind turbines, and battery components could increase renewable energy project costs by 15-25%, potentially slowing the transition to clean energy and affecting climate goals in both the U.S. and countries exporting green technology.
What is the European Union response to Trump tariffs?
The European Union response to Trump tariffs includes coordinated 25% countermeasures on €18.4 billion of strategically selected U.S. goods, acceleration of trade agreements with other partners, €45 billion in support for affected industries, and legal challenges through the WTO.
How are emerging markets affected by the US-China tariff escalation?
Emerging markets face mixed impacts from US-China tariff escalation – some benefit from supply chain diversification (Vietnam, Mexico, India), while others suffer from reduced Chinese demand for raw materials (Brazil, Chile, Indonesia) and general economic uncertainty depressing investment.
What is Trump’s tariff policy toward Mexico and Canada?
Trump’s tariff policy toward Mexico and Canada includes threats to withdraw from the USMCA (the replacement for NAFTA), proposed new tariffs averaging 15% despite existing trade agreements, and demands for enhanced border security measures as conditions for tariff exemptions.
What do economists say about protective tariffs?
Most economists view protective tariffs as inefficient, noting they typically reduce overall economic welfare by increasing consumer prices, protecting less competitive industries, inviting retaliation, and creating deadweight losses through market distortions – though some strategic industries may warrant temporary protection.
How do Trump’s tariffs compare to historical protectionist policies?
Trump’s tariffs differ from historical protectionist policies in their unprecedented scope (targeting multiple major trading partners simultaneously), their implementation during peacetime prosperity rather than economic crisis, and their challenge to established multilateral trade institutions like the WTO.
What are the alternatives to tariffs for addressing trade imbalances?
Alternatives to tariffs for addressing trade imbalances include currency policy adjustments, targeted investment restrictions, intellectual property protection enhancement, export promotion programs, worker retraining initiatives, and negotiated sectoral agreements without broad tariff implementation.
How should businesses prepare for ongoing tariff uncertainty?
Businesses facing tariff uncertainty should develop contingency plans including supplier diversification, strategic inventory management, country-of-origin engineering, pricing strategy adjustments, enhanced forecasting capabilities, and active engagement with trade officials regarding exclusion processes.
What tariff mitigation strategies are most effective for importers?
Effective tariff mitigation strategies for importers include product reclassification (where legally appropriate), foreign trade zone utilization, duty drawback programs for re-exports, first sale rule application, strategic use of bonded warehouses, and pursuit of country-specific exemptions where available.
How can investors position portfolios during trade wars?
Investors navigating trade wars typically reduce exposure to export-dependent companies, increase allocations to domestically-focused businesses, consider commodities as inflation hedges, evaluate currency impacts carefully, and maintain higher cash reserves until policy directions clarify.
What are Trump tariffs and how extensive are they in 2025?
Trump tariffs are import taxes imposed by former U.S. President Donald Trump’s administration on goods from foreign countries. The 2025 tariffs are exceptionally broad, targeting over 60 countries with rates as high as 34% on certain imports, affecting approximately $2.5 trillion in global trade value.
How can I stay updated on Trump tariff news?
The most reliable sources for Trump tariff news include financial publications like Bloomberg, The Wall Street Journal, and Financial Times, as well as government websites such as the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) and the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC).
What specific items are on the Trump tariffs list?
The Trump tariffs list is extensive, covering major categories including:
- Electronic components and consumer electronics
- Pharmaceutical ingredients and finished medications
- Steel, aluminum, and other industrial metals
- Automotive parts and assembled vehicles
- Agricultural products and processed foods
- Textiles, apparel, and footwear
- Renewable energy equipment including solar panels
- Medical devices and diagnostic equipment
How are Trump tariffs affecting the pharmaceutical industry?
Trump tariff on pharma has created significant disruption in global medical supply chains. With approximately 80% of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) sourced globally, the tariffs have increased manufacturing costs by 8-22% across various medication categories. This has raised concerns about drug shortages, price increases, and reduced medication access, particularly in developing nations.
Related Articles:
Quick Commerce India: Unlocking Consumer Minds, Shaping Global Trends 2025