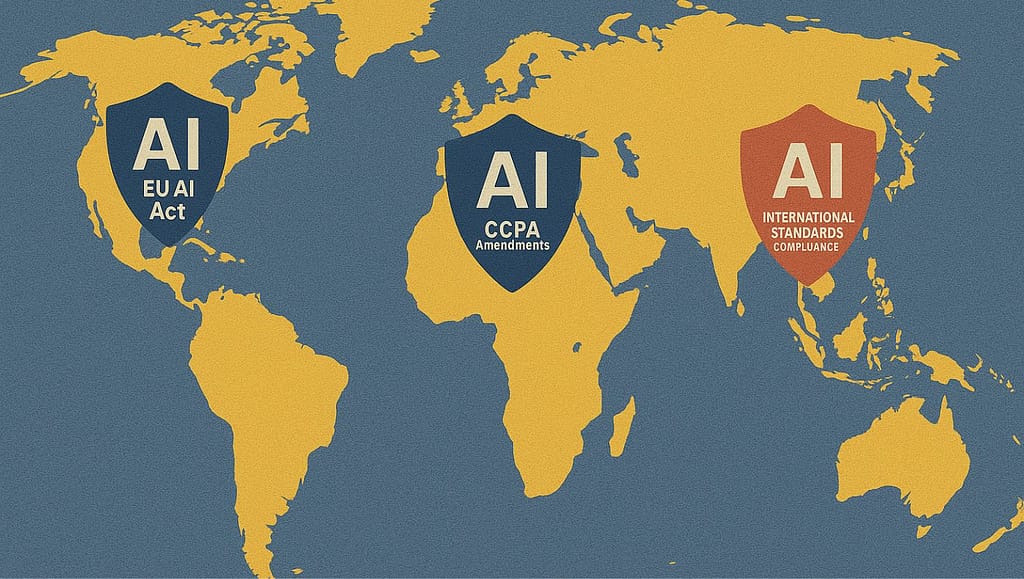
AI Data Regulation: the artificial intelligence regulatory landscape is experiencing unprecedented transformation in 2025, with governments worldwide implementing comprehensive frameworks to govern AI development, deployment, and data usage. As AI systems become increasingly integrated into business operations and daily life, understanding these evolving regulations has become critical for organizations and individuals alike.
The convergence of privacy concerns, ethical AI deployment, and rapid technological advancement has created a complex regulatory environment that businesses must navigate carefully. From the European Union’s groundbreaking AI Act to California’s enhanced privacy protections and emerging international standards, the regulatory framework governing AI is reshaping how companies collect, process, and utilize data in AI systems.
This comprehensive analysis examines the current state of AI regulation in 2025, providing actionable insights for businesses and users navigating this fragmented yet increasingly harmonized global privacy environment.
Understanding the Global AI Regulatory Landscape in 2025
The year 2025 marks a pivotal moment in AI governance, with multiple jurisdictions implementing comprehensive regulatory frameworks simultaneously. Unlike previous technology regulations that developed organically over decades, AI regulation is emerging rapidly and comprehensively across major economic zones.
The Regulatory Convergence Phenomenon
Research indicates that AI regulations worldwide are converging around several key principles: algorithmic accountability, data minimization, user consent, and algorithmic transparency. This convergence reflects shared concerns about AI’s impact on privacy, fairness, and human autonomy, despite different implementation approaches across jurisdictions.
The regulatory landscape now encompasses three primary layers: foundational privacy laws (like GDPR), AI-specific regulations (such as the EU AI Act), and sector-specific requirements (including financial services and healthcare AI rules). This multi-layered approach creates both opportunities for comprehensive protection and challenges for compliance management.
Key Regulatory Drivers Shaping 2025 Policies
Studies show that current AI regulations are primarily driven by four factors: public concern about algorithmic bias, high-profile AI-related privacy breaches, competitive concerns about AI market concentration, and the need to maintain public trust in digital services. These drivers explain why regulations focus heavily on transparency, user control, and algorithmic accountability.
The EU AI Act: Setting Global Standards for AI Governance
The European Union’s AI Act represents the world’s first comprehensive AI regulation, establishing risk-based categories for AI systems and creating binding obligations for AI developers and deployers.
Understanding EU AI Act Risk Categories
The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems into four risk levels: prohibited practices, high-risk applications, limited-risk systems, and minimal-risk applications. Each category carries specific compliance obligations, from complete prohibition of certain AI uses to transparency requirements for user-facing systems.
High-risk AI systems, including those used in employment decisions, credit scoring, and law enforcement, face the most stringent requirements. These systems must undergo conformity assessments, maintain detailed documentation, and implement robust human oversight mechanisms. For businesses operating in or serving EU markets, understanding these risk categories is essential for compliance planning.
Data Protection Requirements Under the AI Act
The AI Act introduces specific data governance requirements that complement existing GDPR obligations. AI systems must implement data quality management systems, ensuring training data is relevant, representative, and free from harmful bias.
Additionally, the regulation requires organizations to establish clear data lineage documentation, enabling regulators and users to understand how personal data flows through AI systems.
Enforcement and Penalty Structure
Violations of the EU AI Act can result in fines up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. The enforcement framework delegates primary responsibility to national authorities while maintaining oversight through the European AI Board. This structure ensures consistent application across member states while allowing for local implementation flexibility.
California CCPA Amendments: Strengthening AI Privacy Protections
California’s Consumer Privacy Act amendments in 2025 introduce specific provisions for AI systems, reflecting the state’s continued leadership in privacy regulation.
Enhanced Automated Decision-Making Rights
The 2025 CCPA amendments grant California consumers new rights regarding automated decision-making systems. Consumers now have the right to know when AI systems are used in decisions affecting them, understand the logic behind these decisions, and request human review of automated determinations. These rights apply to any business processing California residents’ data, regardless of the company’s location.
AI Training Data Transparency Requirements
Under the amended CCPA, businesses using personal information for AI training must provide detailed disclosures about data usage. These disclosures must specify the categories of personal information used, the sources of training data, and the purposes for which AI models are developed. Additionally, consumers gain the right to opt out of having their personal information used for AI training purposes.
Biometric and Sensitive Data Protections
The 2025 amendments establish enhanced protections for biometric identifiers and sensitive personal information used in AI systems. Businesses must obtain explicit consent before processing biometric data for AI training, implement additional security measures for sensitive information, and provide consumers with granular control over how their sensitive data is used in automated systems.
International Frameworks: ISO Standards and NIST Guidelines
Global standardization bodies are developing comprehensive frameworks to support AI governance and compliance across jurisdictions.
ISO 27001/27701 Integration with AI Systems
The International Organization for Standardization has updated ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 standards to address AI-specific privacy and security requirements. These updated standards provide organizations with systematic approaches to managing AI-related privacy risks while maintaining compatibility with existing information security management systems.
ISO 27701’s 2025 updates include specific controls for AI data processing, algorithmic transparency requirements, and automated decision-making governance procedures. Organizations implementing these standards benefit from internationally recognized frameworks that facilitate compliance with multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
NIST AI Risk Management Framework Evolution
The National Institute of Standards and Technology’s AI Risk Management Framework has evolved significantly in 2025, incorporating lessons learned from early AI deployments and regulatory feedback. The updated framework provides detailed guidance on measuring and mitigating AI risks throughout the system lifecycle.
Key framework updates include enhanced bias detection methodologies, improved fairness measurement techniques, and standardized approaches to AI system documentation. The framework’s risk-based approach aligns with regulatory trends worldwide, making it valuable for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions.
How AI Regulations Impact Different Platform Types
AI regulations affect different types of platforms and applications in varying ways, requiring tailored compliance approaches.

Consumer-Facing AI Applications
Consumer AI applications, including chatbots, recommendation systems, and personal assistants, face significant transparency and consent requirements under new regulations. These applications must provide clear notifications when AI is being used, offer meaningful choices about data processing, and implement user-friendly privacy controls.
The regulatory focus on consumer applications reflects concerns about manipulation, addiction, and unauthorized data collection. Compliance requires implementing privacy-by-design principles, conducting regular algorithmic audits, and maintaining comprehensive user documentation.
Enterprise AI Solutions
Business-to-business AI solutions face different regulatory challenges, particularly regarding data sharing agreements, liability allocation, and cross-border data transfers. Enterprise AI providers must implement robust data governance frameworks, establish clear contractual terms for AI services, and ensure compatibility with customers’ regulatory obligations.
Healthcare and Financial AI Systems
AI systems in regulated industries face additional sector-specific requirements beyond general AI regulations. Healthcare AI must comply with HIPAA, medical device regulations, and clinical trial requirements, while financial AI systems must meet banking regulations, fair lending laws, and financial privacy requirements.
Compliance Challenges in a Fragmented Regulatory Environment
The proliferation of AI regulations creates significant compliance challenges for organizations operating globally.
Managing Multi-Jurisdictional Requirements
Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions must navigate overlapping and sometimes conflicting regulatory requirements. Effective compliance strategies involve identifying the highest common denominator of requirements, implementing comprehensive governance frameworks, and maintaining detailed documentation to satisfy various regulatory regimes.
Resource Allocation and Compliance Costs
Studies indicate that AI compliance costs can represent 15-25% of AI development budgets for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions. These costs include legal counsel, technical implementations, ongoing monitoring, and regulatory reporting requirements. Organizations must balance compliance investments with innovation goals while maintaining competitive positioning.
Third-Party Vendor Management
Many organizations rely on third-party AI services, creating additional compliance complexity. Vendor management frameworks must address data processing agreements, liability allocation, audit rights, and termination procedures. Due diligence requirements include assessing vendors’ compliance programs, data security measures, and ability to support customer compliance obligations.
Emerging Trends and Future Regulatory Developments
Several trends are shaping the future evolution of AI regulation beyond 2025.
Harmonization Efforts and International Cooperation
International organizations are working to harmonize AI governance approaches, reducing compliance complexity for global organizations. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) AI Principles and ongoing G7 discussions suggest movement toward greater regulatory alignment, though significant differences remain between jurisdictions.
Sectoral Regulation Expansion
Regulatory authorities are developing sector-specific AI rules for industries including transportation, education, and public safety. These specialized regulations address unique risks and requirements within specific industries while building upon foundational AI governance frameworks.
Technological Solutions for Compliance
Emerging technologies, including privacy-enhancing technologies and automated compliance monitoring systems, are helping organizations manage regulatory requirements more effectively. These solutions include automated policy enforcement, continuous compliance monitoring, and privacy-preserving analytics for regulatory reporting.
Practical Compliance Strategies for 2025
Organizations can implement several strategies to effectively navigate the current regulatory environment.
Building Comprehensive AI Governance Programs
Effective AI governance programs integrate legal, technical, and business considerations into cohesive frameworks. Key components include executive oversight, cross-functional governance committees, regular risk assessments, and continuous monitoring procedures. These programs must adapt to evolving regulatory requirements while supporting business objectives.
Implementing Privacy-by-Design Principles
Privacy-by-design implementation involves incorporating privacy considerations throughout the AI development lifecycle. This includes data minimization in training datasets, implementing differential privacy techniques, and designing user interfaces that promote informed consent and meaningful choice.
Documentation and Audit Trail Management
Comprehensive documentation is essential for regulatory compliance and enables organizations to demonstrate good faith efforts to comply with applicable requirements. Documentation should include system design decisions, data source information, algorithmic testing results, and ongoing monitoring activities.
Regional Variations and Local Implementations
Different regions are implementing AI regulations with unique characteristics reflecting local priorities and legal traditions.
Asia-Pacific Regulatory Approaches
Countries in the Asia-Pacific region are developing AI governance frameworks that emphasize economic development alongside privacy protection. Singapore’s AI governance framework focuses on industry self-regulation and innovation facilitation, while Japan’s AI strategy emphasizes human-centric AI development and international cooperation.
Americas Regional Developments
Beyond California’s leadership, other American jurisdictions are developing AI-specific regulations. Canada’s proposed AI and Data Act would establish comprehensive AI governance requirements, while several U.S. states are considering AI-specific legislation addressing algorithmic bias and automated decision-making.
African Union AI Strategy
The African Union’s AI strategy emphasizes leveraging AI for sustainable development while protecting citizens’ rights. The strategy includes provisions for data sovereignty, algorithmic accountability, and capacity building to ensure African countries can participate effectively in the global AI economy.
Meta AI just hit the panic button on AI
Industry-Specific Compliance Considerations
Different industries face unique AI regulatory challenges requiring specialized approaches.
Technology Sector Adaptations
Technology companies developing AI platforms must implement comprehensive compliance programs addressing multiple use cases and customer requirements. These programs must be scalable, technically robust, and capable of supporting diverse regulatory obligations across different markets and applications.
Financial Services AI Compliance
Financial institutions using AI must navigate complex regulatory environments including banking regulations, consumer protection laws, and fair lending requirements. Compliance strategies must address model risk management, algorithmic bias prevention, and transparency requirements while maintaining competitive advantage.
Healthcare AI Regulatory Navigation
Healthcare AI applications face unique challenges including medical device regulations, clinical trial requirements, and patient privacy protections. Compliance requires close coordination between technical teams, clinical experts, and regulatory specialists to ensure patient safety and regulatory adherence.
Navigating AI Regulation Success in 2025
The AI regulatory landscape in 2025 represents both challenge and opportunity for organizations worldwide. While the complexity of multi-jurisdictional requirements creates compliance burdens, the emergence of comprehensive frameworks also provides clarity and predictability for AI development and deployment.
Success in this environment requires proactive engagement with regulatory developments, investment in comprehensive governance programs, and commitment to ethical AI development practices. Organizations that view regulatory compliance as a competitive advantage rather than a burden will be best positioned to thrive in the evolving AI economy.
The key to effective compliance lies in building flexible, scalable governance frameworks that can adapt to evolving requirements while supporting innovation and growth. By understanding the regulatory landscape, implementing robust compliance programs, and maintaining commitment to ethical AI development, organizations can navigate successfully through 2025 and beyond.
Ready to ensure your AI systems comply with 2025 regulations?
Start by conducting a comprehensive regulatory assessment of your current AI applications and developing a tailored compliance strategy that addresses your specific operational requirements and risk profile.